Ping: The Essential Tool for Network Connectivity Testing
Created on 17 January, 2025 • Checker Tools • 81 views • 2 minutes read
Ping is a fundamental network utility used to test the reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol (IP) network.
What is Ping?
Ping is a fundamental network utility used to test the reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol (IP) network. By sending data packets to a specific IP address and waiting for a response, Ping helps determine whether a device is accessible and how quickly it can communicate over the network. This simple yet powerful tool is essential for network troubleshooting, performance monitoring, and ensuring reliable connectivity.
Why is Ping Important?
Understanding the significance of Ping is crucial for anyone involved in network management or IT support. It serves multiple purposes, including:
- Connectivity Verification: Ping helps confirm whether a device is online and reachable.
- Latency Measurement: By calculating the round-trip time (RTT) for packets, Ping provides insights into network performance.
- Troubleshooting Tool: When connectivity issues arise, Ping can help identify where the problem lies in the network.
How Does Ping Work?
The Mechanics of the Ping Command
When you issue a Ping command, your device sends an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request to the target host. The process involves several key steps:
- Sending Echo Requests: The source device sends ICMP packets to the specified IP address.
- Receiving Echo Replies: If the target host is reachable, it responds with ICMP Echo Reply packets.
- Calculating Round-Trip Time: The time taken for the request to reach the target and for the reply to return is measured in milliseconds (ms).
This straightforward mechanism allows users to assess both connectivity and latency effectively.
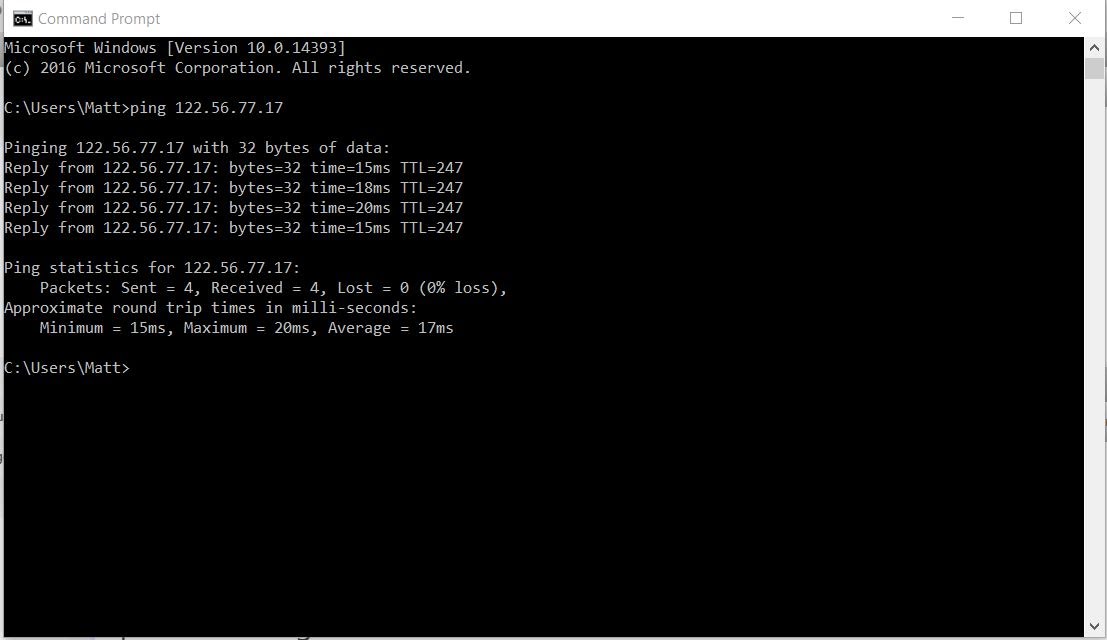
Interpreting Ping Results
The output of a Ping command provides valuable information about network performance. Key metrics include:
- Response Time: Indicates how long it took for the reply to return.
- Packet Loss: Shows if any packets were lost during transmission, which can signal network issues.
- TTL (Time to Live): This value indicates how many hops (routers) the packet has traversed before reaching its destination.
By analyzing these results, network administrators can diagnose connectivity problems and optimize performance.
Practical Uses of Ping
1. Checking Network Connectivity
The most common use of Ping is to verify connectivity between devices. Whether you're troubleshooting a local network or testing internet access, Ping provides a quick way to confirm that devices can communicate.
2. Diagnosing Network Issues
When connectivity problems arise, Ping is often the first tool used in troubleshooting. By sending pings to various points in a network, IT professionals can pinpoint where issues may be occurring, such as identifying faulty hardware or misconfigured settings.
3. Monitoring Network Performance
Regularly using Ping can help monitor the health of a network over time. By tracking response times and packet loss rates, organizations can identify trends and potential performance bottlenecks before they escalate into more significant issues.
Conclusion: Leveraging Ping for Optimal Network Performance
In today's digital landscape, maintaining reliable network connectivity is essential for businesses and individuals alike. Understanding how to use Ping effectively can empower users to troubleshoot issues, monitor performance, and ensure seamless communication across devices.By incorporating regular Ping tests into your network management routine, you can proactively address potential problems and enhance overall performance. Embrace this powerful tool today and unlock the full potential of your network!