DNS Lookup: Understanding the Backbone of Internet Browsing
Created on 15 January, 2025 • Checker Tools • 129 views • 4 minutes read
Learn everything about DNS lookup, its role in website performance, and its impact on SEO. Discover types, best practices, and tips to optimize DNS for better rankings.
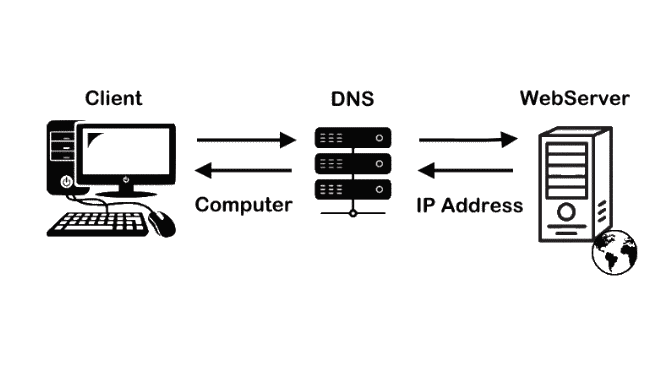
The Domain Name System (DNS) is an essential component of the internet that allows us to access websites without needing to remember complex IP addresses. A DNS lookup is the process that translates domain names (like example.com) into IP addresses that computers use to locate web servers. This guide will break down the concept of DNS lookup, its types, and its importance in website performance and SEO.What Is DNS Lookup?
DNS Lookup is the process through which a domain name is converted into its corresponding IP address. When you enter a URL in your browser, a DNS lookup takes place to retrieve the IP address of the server hosting the website.
Why Is DNS Lookup Important?
It ensures that users can access websites using easy-to-remember domain names.
It acts as a "phone book" for the internet, connecting users to the correct server.
Faster DNS lookups contribute to improved website loading times, which is crucial for SEO and user experience.
How DNS Lookup Works
The DNS lookup process involves multiple steps to translate a domain name into an IP address. Here's how it works:
1. The User Request
When a user types a URL (e.g., www.example.com) into their browser, the browser sends a request to the DNS resolver.
2. Recursive DNS Resolver
The resolver acts as a middleman, querying different servers to find the correct IP address for the domain.
3. Querying the DNS Servers
The resolver queries:
Root DNS Server: Directs the query to the appropriate Top-Level Domain (TLD) server.
TLD Server: Provides the address of the authoritative server for the domain.
Authoritative DNS Server: Returns the IP address of the requested domain.
4. Returning the IP Address
Once the IP address is retrieved, the browser connects to the server, and the webpage is loaded.
Types of DNS Lookups
There are two main types of DNS lookups, each serving a specific purpose:
1. Forward DNS Lookup
This is the standard DNS query where a domain name is translated into its corresponding IP address.
Example:
Input: www.example.com
Output: 192.168.1.1
2. Reverse DNS Lookup
This process is the opposite of forward DNS lookup. It involves finding the domain name associated with a specific IP address.
Example:
Input: 192.168.1.1
Output: www.example.com
The Role of DNS Lookup in Website Performance
1. Faster Page Load Times
A faster DNS lookup process reduces the time it takes to connect to a server, ensuring quicker page load speeds. Since page speed is a significant SEO ranking factor, optimizing DNS can directly improve your search engine rankings.
2. Better User Experience
Slow DNS resolution can frustrate users and increase bounce rates. A smooth DNS lookup process enhances user satisfaction, keeping visitors engaged with your site.
3. Reliable Website Access
A properly functioning DNS ensures your website remains accessible to users globally. Downtime or errors in DNS can lead to lost traffic and potential SEO penalties.
DNS Lookup and SEO: Why It Matters
DNS lookup directly influences your website’s speed and reliability, which are critical factors for SEO. Here’s why it matters:
1. Website Speed
Google prioritizes fast-loading websites, and a slow DNS resolution can delay page load times. Optimizing DNS lookup ensures your site loads quickly, improving both user experience and rankings.
2. Mobile Optimization
Mobile users expect fast and seamless browsing. Optimized DNS resolution can prevent delays, ensuring your website performs well on mobile devices.
3. Security and Trust
DNS issues like spoofing or cache poisoning can harm your site's credibility. A secure and well-maintained DNS setup protects your site and builds trust with users and search engines.
Best Practices for Optimizing DNS Lookup
To improve your DNS lookup process and enhance your website’s performance, follow these best practices:
1. Use a Reliable DNS Provider
Choose a reputable DNS provider that offers fast resolution times and robust security features.
2. Enable DNS Caching
DNS caching stores query results temporarily, reducing the time needed for future lookups.
3. Monitor and Optimize DNS Settings
Regularly monitor DNS performance and optimize settings to prevent bottlenecks and downtime.
4. Leverage Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
CDNs distribute website content across multiple servers, reducing the time needed to retrieve DNS records.
5. Reduce CNAME Records
While CNAME records simplify domain management, they can increase DNS lookup times. Minimize their use to improve speed.
Common DNS Lookup Issues and How to Fix Them
1. DNS Resolution Errors
These occur when the DNS resolver cannot find the requested domain's IP address.
Solution: Check your DNS settings and ensure the domain is correctly configured.
2. Slow DNS Lookup Times
A slow DNS lookup increases the time it takes for a webpage to load.
Solution: Use a faster DNS provider, enable caching, or leverage a CDN.
3. DNS Server Downtime
If the DNS server goes down, your website becomes inaccessible.
Solution: Use a DNS provider with high uptime guarantees and failover support.
Conclusion
DNS lookup is a fundamental process that ensures users can access websites effortlessly. Its speed and reliability directly impact user experience and SEO performance. By understanding how DNS lookup works and implementing best practices to optimize it, you can enhance your website’s performance, boost your rankings, and create a better experience for your visitors.
Start optimizing your DNS setup today and reap the benefits of faster, more reliable web performance!